
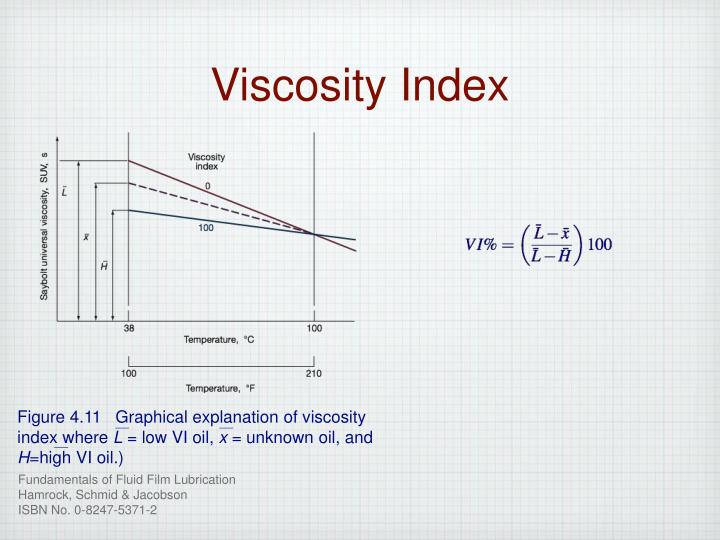
If even a quality 22 weight hydraulic oil can barely pour at -27° C, these arctic oils will still exit an upside down beaker at -60° C or colder! These oils often have the words “arctic” or “blue” in their names, but they’re always synthetic oils formulated to flow at extremely low temperatures. However, you can imagine this oil will be pretty thick and difficult to push at -20° C if at seven degrees colder, it’s barely able to be called a fluid.įor machines to be happy in conditions similar to the winter of 2013-2014, a different kind of oil should be used. A premium 22 cSt oil with a respectable VI of 100 might have a pour point of -27° C. With hydraulic oil, a viscosity index of 100 is considered excellent (although automotive engine oil VI numbers can approach 200).Ī caveat about viscosity index and cold temperatures-often, the oil chemistry specific to the creation of high viscosity index doesn’t always translate into a lower pour point, which is really what we’re concerned with in cold temperatures. The higher the viscosity index, the higher the resistance to change in viscosity. It is often measured by comparing the change in viscosity between 40° C and 100° C. Viscosity Index is a dimensionless number to describe an oil’s resistance to a change in viscosity when subjected to a change in temperature. So what will the viscosity of a 22 weight oil be at minus twenty? Well, it depends…. This fluid could be appropriate in most mobile applications, but we should first consider a 22 centistoke oil is rated so at 40° C, not -20° F. Half of the consideration is with rated viscosity, such as “22 weight” oil, which is considered to be a low viscosity fluid by most. The solution to cold weather viscosity problems is to choose appropriate hydraulic fluid. I sometimes see cold hydraulic systems with cylinders that retract slower than they extend because of the extra pressure drop created by flow intensification of cold oil. The thicker the oil, the harder it is to pump, and if plumbing distance is long with marginal diameter, a lot of energy can be lost to pumping, leaving little left over to perform work. Hydraulic fluid is highly susceptible to viscosity changes based on temperature, especially if the machine has been sitting idle in the cold. Regardless, even if the seals can hold up from November to March, they won’t make it any easier to pump that ketchup. Luckily, seal manufacturers make solutions for arctic conditions, such as low-temp Nitrile or Viton. Some concern in frigid temperature operation is with seal material, and whether the seal material can avoid becoming brittle. However, the concern is when these metal parts either rub against other metal parts, or the metal parts are attempting to push a fluid as thick as ketchup. Luckily most hydraulic parts are made from iron or steel, which tend to not care about ambient temperature. These fluids is not equal for all directions (seen in cases such asĭie swell).As one of the longest, coldest winters on record comes to an end (or doesn’t come to an end, in this case), I consider how all the hydraulic machines must have fared throughout the brutal outdoor conditions we’ve experienced in the past four months. To the fact that when you measure the 'viscosity' of a fluid, youĪre only measure one direction in the stress tensor, which for The 'viscous'Ĭlosure term falls apart for these fluids. Navier Stokes equations on non-newtonian fluids. This becomes very apparent when attempting to use the Newtonian fluids, because in fact some fluids do not have constant Let it be noted that 'viscosity' is only a term applied to
Yield a fluids viscosity, although the results may beĭefinition- the state of being thick, sticky, and semifluid in In simple shear flow, and test it in elongation. There are typically two ways to measure fluid viscosity, test it Of fluids and cannot be directly linked to fluid parameters. Of the fluid (in one tensorial direction).

Viscosity is the measure of the shear stress vs the shear strain


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
